Infrared Thermometer Instruction Manual: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide serves as your essential resource for understanding and effectively using your infrared thermometer. It provides clear instructions and important considerations to ensure accurate temperature measurements for various applications.

Infrared thermometers are invaluable tools for non-contact temperature measurement, offering a safe and efficient way to determine surface temperatures. These devices work by detecting the infrared energy emitted from an object, converting it into a temperature reading displayed on a screen.
This technology allows for quick measurements without the need to physically touch the object, making it ideal for various applications. From checking the temperature of a baby bottle to assessing HVAC system performance, infrared thermometers provide versatile solutions.
Understanding the basic principles of how these thermometers function is crucial for accurate usage. Factors such as emissivity, distance, and ambient temperature can influence readings, requiring careful consideration when interpreting results. With proper technique, infrared thermometers deliver reliable temperature data for informed decision-making.
Understanding the Purpose of the Manual

This manual serves as a comprehensive guide to operating your infrared thermometer effectively and safely. Its primary purpose is to provide you with the necessary information to understand the device’s functions, capabilities, and limitations.
By carefully studying this manual, you’ll learn how to obtain accurate temperature readings, interpret the displayed data, and maintain the thermometer for optimal performance. It covers essential topics such as measurement techniques, unit conversions (Fahrenheit and Celsius), and safety precautions.
Furthermore, this manual addresses common questions and troubleshooting scenarios you might encounter while using the infrared thermometer. Whether you’re a first-time user or an experienced professional, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to maximize the benefits of your device and ensure reliable temperature measurements across various applications, minimizing potential errors.

Key Features and Applications
Infrared thermometers offer non-contact temperature measurement, ideal for various applications. Key features include rapid readings, safety, and versatility in HVAC, body temperature assessment, and surface temperature monitoring.
Measuring Surface Temperature
Infrared thermometers excel at measuring surface temperatures without physical contact. This capability is invaluable in various industrial and domestic settings. To accurately measure surface temperature, ensure the thermometer is held at the correct distance-to-spot ratio, as specified in the manual. This ratio determines the area being measured; maintaining the recommended distance ensures the reading reflects the intended surface area.
Consider the emissivity of the surface being measured. Emissivity refers to a material’s ability to emit infrared radiation. Different materials have different emissivity values, which can affect the accuracy of the temperature reading. Adjust the thermometer’s emissivity setting if possible, or consult emissivity tables for specific materials.
Avoid measuring shiny or reflective surfaces, as they can produce inaccurate readings due to reflected infrared radiation from surrounding objects. For such surfaces, apply a matte black tape or paint to increase emissivity and improve accuracy. Always ensure the target area is free from obstructions like dust or moisture, which can also affect the reading.
Body Temperature Measurement (Forehead and Ear)
Infrared thermometers designed for body temperature measurement offer two convenient methods: forehead and ear readings. Forehead measurements involve pointing the thermometer at the center of the forehead, maintaining the specified distance. Ensure the forehead is clean, dry, and free from hair or sweat, as these can affect accuracy. Swipe across the forehead if the device requires, following the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal results.
Ear measurements, suitable for adults and children, require gently inserting the thermometer probe into the ear canal. Ensure the ear canal is clear of wax buildup. Gently pull the ear back to straighten the ear canal for accurate readings, especially in infants and young children. Note that ear measurements may not be suitable for individuals with ear infections or those who have undergone ear surgery.
Always consult the specific model’s manual for detailed instructions and age-specific guidelines. Remember that body temperature can vary based on factors like activity level and time of day.
HVAC Applications
Infrared thermometers are invaluable tools in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) applications. Their non-contact nature allows technicians to quickly and safely measure surface temperatures of various components without physical contact. This is crucial for diagnosing system performance and identifying potential issues.
Common HVAC applications include checking the temperature of air vents to ensure proper airflow and distribution, verifying the temperature of refrigerant lines to assess cooling efficiency, and identifying hot spots in electrical panels or motors associated with HVAC systems. Technicians can also use infrared thermometers to detect insulation deficiencies by measuring temperature variations on walls and ceilings.
When using an infrared thermometer in HVAC, consider the emissivity of the target surface. Some materials reflect more infrared energy than others, affecting accuracy. Adjust the emissivity setting on the thermometer, if available, or use emissivity tape to ensure precise readings. Always follow safety precautions and consult the equipment’s manual for optimal performance.
Operating Instructions
This section provides detailed guidance on the proper operation of your infrared thermometer. It covers essential techniques, settings adjustments, and safety precautions to ensure accurate and reliable temperature measurements.
Measurement Techniques: Angle and Distance
Achieving accurate temperature readings with an infrared thermometer depends significantly on proper technique, particularly concerning the angle and distance from the target object. The infrared thermometer measures the surface temperature of an object by sensing the emitted, reflected, and transmitted energy.
Maintaining the correct angle is crucial. Ensure the thermometer is perpendicular to the surface being measured. An angled approach can lead to inaccurate readings as the device may capture infrared radiation from surrounding areas.
Distance also plays a vital role. Each thermometer has a specific distance-to-spot ratio, indicating the area being measured at a given distance. Exceeding the recommended distance may result in the thermometer averaging the temperature over a larger, unintended area, thus compromising accuracy. Conversely, being too close might not allow the device to focus correctly.
Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for the optimal distance to achieve the most precise measurement. Experiment with different distances within the recommended range to observe any variations in readings and determine the sweet spot for your specific application. Consistent angle and distance are key to reliable results.
Switching Between Fahrenheit and Celsius
Many infrared thermometers offer the convenience of displaying temperature readings in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Understanding how to switch between these units is essential for users accustomed to a particular scale or when comparing measurements from different sources.
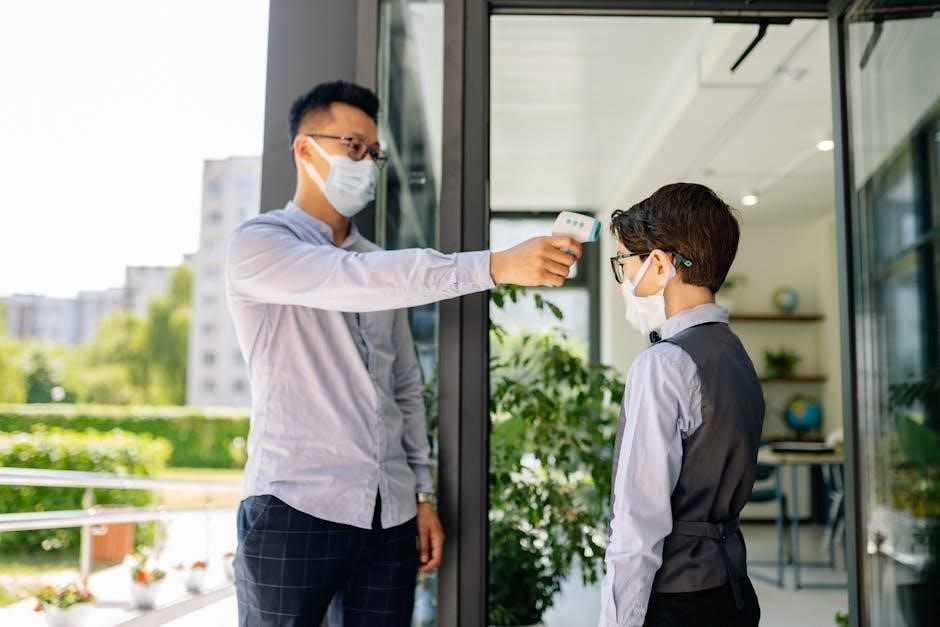

The method for changing the temperature unit typically involves pressing a specific button or combination of buttons on the device. Refer to your infrared thermometer’s instruction manual for precise instructions, as the process can vary between models. Look for a button labeled “Mode,” “Set,” or a button with a degree symbol (°F/°C).
In some models, you might need to access a settings menu by holding down a button for a few seconds. Once in the menu, navigate to the temperature unit option and select your preferred scale.
After changing the unit, ensure the display reflects the correct scale before taking measurements. Some thermometers may also have a small indicator icon to show which unit is currently active. If you encounter difficulties, consult the troubleshooting section of the manual or contact the manufacturer for assistance. Properly setting the temperature unit ensures accurate interpretation of readings.
Using the Laser Pointer (If Applicable)
Many infrared thermometers are equipped with a laser pointer to aid in aiming and targeting the measurement area. However, it’s crucial to understand the laser’s function and safety precautions before use. The laser is primarily a visual guide and does not directly contribute to the temperature measurement itself.
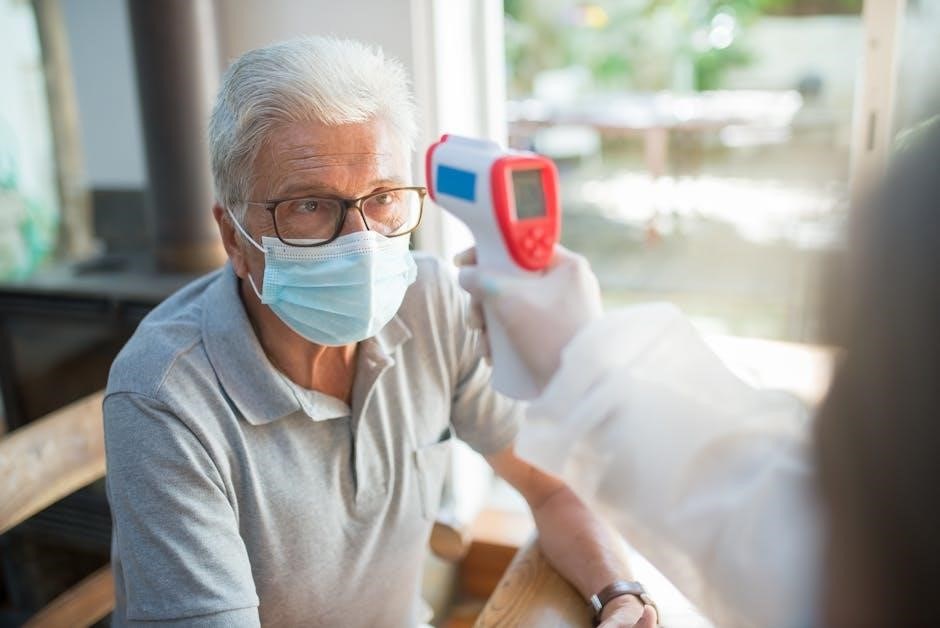

To activate the laser, typically, there’s a dedicated button on the thermometer’s handle or body, often marked with a laser symbol. Pressing this button will project a visible red dot, indicating the approximate center of the area being measured. It’s important to remember that the actual measurement area is determined by the distance-to-spot ratio, as detailed elsewhere in this manual.
Always exercise caution when using the laser. Never point the laser beam directly into anyone’s eyes, including animals. Avoid reflecting the laser beam off shiny surfaces, as this can also pose a hazard. The laser is intended solely for aiming purposes. When not in use, ensure the laser is switched off to conserve battery life and prevent accidental activation.
Refer to the safety guidelines in this manual and on the thermometer itself for further precautions.

Specific Models and Manufacturers
This section details information regarding specific infrared thermometer models and their respective manufacturers. Model-specific instructions and features will be highlighted for popular brands like Fluke and Jumper Medical, ensuring optimal usage.
Fluke Infrared Thermometers
Fluke infrared thermometers are renowned for their precision and reliability in non-contact temperature measurement. The Fluke 561 and 576 models, in particular, are designed for diverse applications, including HVAC and industrial settings. These thermometers determine an object’s surface temperature by measuring the amount of infrared energy radiated, reflected, and transmitted.
This section will cover specific instructions applicable to Fluke infrared thermometers. It will include guidance on navigating the user interface, understanding measurement parameters, and performing accurate readings. Note that some Japanese models may indicate Celsius only. For any inquiries or support, Fluke offers comprehensive customer service; contact details are available in the full manual.
Fluke thermometers are built to provide consistent and dependable results, making them essential tools for professionals across various industries. Always consult the full instruction manual for detailed safety information and calibration guidelines.
Jumper Medical Equipment (JPD-FR203)
The Jumper Medical Equipment JPD-FR203 infrared thermometer is a non-contact device specifically designed for measuring human body temperature. This model is particularly suited for obtaining forehead temperatures and is safe for use on people of all ages, including infants and children. It is manufactured by Shenzhen Jumper Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., located in Shenzhen, China.
The JPD-FR203 is intended for quick and easy temperature readings without physical contact, reducing the risk of cross-contamination. It can also measure the temperature of objects like baby bottles or bathwater by using the surface temperature mode. This section will provide detailed instructions on how to accurately use the JPD-FR203, including how to switch between modes and interpret the readings.
Always refer to the full user manual for safety precautions and maintenance guidelines to ensure accurate and reliable performance. Understanding the device’s features and proper usage will provide the best possible experience when using the JPD-FR203.

Important Considerations
Ensuring accurate readings involves understanding factors influencing measurement. Consistent angle, distance, and a steady hand are crucial. Movement impacts temperature readings, emphasizing the need for careful technique.
Impact of Movement on Readings
Maintaining a steady hand is paramount when using an infrared thermometer, as movement can significantly impact the accuracy of temperature readings. The device relies on capturing the infrared energy emitted by the target surface, and any shift in position during the measurement process can distort this capture.
Even slight movements can cause the thermometer to register infrared radiation from unintended surrounding areas, leading to inaccurate results. Therefore, it is essential to hold the thermometer as still as possible throughout the measurement, ensuring that it remains focused solely on the intended target.
To mitigate the effect of movement, consider stabilizing your arm or hand against a solid surface. Bracing yourself in this manner can greatly reduce unintentional shifts and improve the reliability of your temperature readings. Remember, a stable measurement yields a more accurate result.
Practicing a steady technique will quickly become second nature, leading to more consistent and trustworthy temperature assessments in all your applications.